Why Deleting Files Doesn't Always Free Up Storage Space on Windows & How to Fix It
Explore the conundrum of why deleting files doesn't always result in reclaimed storage space on Windows devices. Navigate potential risks, explore effective solutions, and harness the capabilities of MyRecover for seamless file recovery.
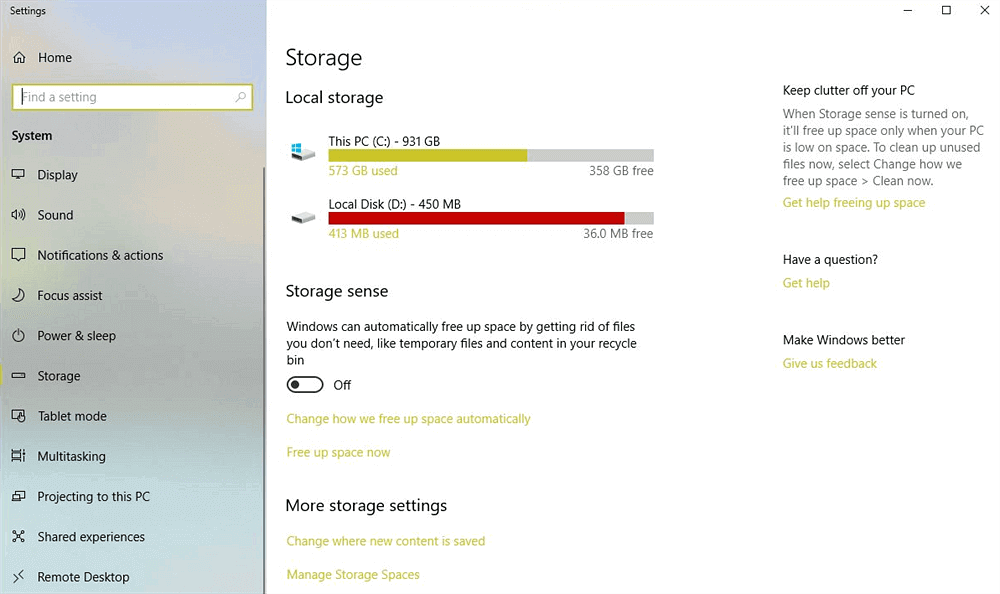
In the digital age, managing storage space is a perpetual challenge for Windows users. Despite conscientious efforts to delete unnecessary files, many find themselves puzzled when their storage space remains stagnant or even decreases.
In this comprehensive guide, we unravel the mysteries behind why deleting files doesn't always free up storage space on Windows systems. We delve into the potential reasons, assess associated risks, and equip users with practical solutions to optimize storage utilization.
Possible Reasons Why Deleting Files Doesn't Free Up Storage Space:
The perplexing phenomenon of deleted files persisting on the storage drive can be attributed to several underlying factors:
- Temporary Files and Caches: Windows accumulates temporary files and caches over time, which continue to occupy disk space even after deletion.
- Files in Recycle Bin: Files deleted and moved to the Recycle Bin may still consume storage until permanently deleted.
- System Restore Points: Windows creates system restore points that reserve disk space for system backups, limiting available storage.
- Large Media Files: Unnecessary large media files, such as videos and photos, may consume significant disk space.
- Fragmented Disk Space: Fragmentation of files and disk space can lead to inefficient storage utilization, hindering the reclaiming of space.
Understanding these factors is essential to devising effective strategies for reclaiming storage space on Windows systems.
Potential Risks of Deleting Files Doesn’t Free Up Storage Space:
The inability to free up storage space poses significant risks and challenges for Windows users:
- Decreased Performance: Insufficient storage space can lead to system slowdowns, decreased performance, and unresponsiveness.
- Data Loss: Inadequate storage space increases the risk of data loss, as users may inadvertently overwrite or delete critical files due to lack of space.
- Limited Functionality: Storage constraints limit the installation of new applications, updates, and system upgrades, impeding productivity and functionality.
Addressing these risks requires proactive measures to optimize storage utilization and ensure a seamless computing experience.
Feasible Fixes to Free Up Windows Storage Space:
1. Temporary Files:
Background: Temporary files, including caches and logs, accumulate over time and occupy disk space.
Fix: Run Disk Cleanup utility to scan and remove temporary files, including system caches, logs, and other temporary data.
2. Files in Recycle Bin:
Background: Deleted files are moved to the Recycle Bin and continue to occupy disk space until permanently deleted.
Fix: Empty the Recycle Bin regularly to permanently delete files and free up storage space on the disk.
3. System Restore Points:
Background: Windows creates system restore points to facilitate system recovery in case of errors or failures.
Fix: Adjust the System Protection settings to reduce the amount of disk space allocated for system restore points or disable System Protection for non-system drives.
4. Large Media Files:
Background: Large media files, such as videos and high-resolution images, consume significant disk space.
Fix: Use disk space analysis tools to identify large files and folders, then manually delete or relocate unnecessary media files to free up storage space.
5. Fragmented Disk Space:
Background: Fragmentation occurs when files are stored in non-contiguous clusters on the disk, leading to inefficient storage utilization.
Fix: Run the Disk Defragmenter tool to analyze and defragment fragmented files, optimizing disk space allocation and improving system performance.
Recovering Cleaned Files on Windows with MyRecover:
MyRecover emerges as a lifeline for users facing data loss due to inadvertent file deletion or cleaning operations. Its key features include:
- Intuitive Interface: MyRecover boasts a user-friendly interface, making file recovery accessible to users of all skill levels.
- Advanced Algorithms: Utilizes advanced algorithms to scan storage devices and recover deleted files efficiently.
- Comprehensive File Support: Capable of recovering a wide range of file types, including documents, photos, videos, and more.
- Preview Functionality: Allows users to preview recovered files before restoration, ensuring accurate recovery.
- Secure Recovery: Ensures secure recovery processes, safeguarding against data loss and corruption.
To recover cleaned files using MyRecover, follow these steps:
Download and Install MyRecover: Visit the official website of MyRecover and download the setup file. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the software on your Windows system.
Launch MyRecover: After installation, launch the MyRecover application from the desktop or Start menu.
Select Scan Location: In the MyRecover interface, select the drive or location from which files were cleaned or deleted.
Initiate Scan: Click on the "Scan" button to initiate the scanning process. MyRecover will perform a thorough scan of the selected drive to identify deleted files.
Preview Recoverable Files: Once the scan is complete, MyRecover will display a list of recoverable files. You can preview the files to ensure their integrity and select the ones you want to recover.
Recover Files: After previewing the files, select the desired files and click on the "Recover" button. MyRecover will prompt you to choose a destination folder to save the recovered files.
Complete Recovery: Once the recovery process is complete, navigate to the destination folder to access the recovered files.
In Conclusion:
Navigating the intricacies of storage management on Windows systems requires understanding the factors contributing to ineffective storage utilization. By identifying potential reasons why deleting files doesn't free up storage space, users can implement practical solutions to optimize storage utilization and mitigate associated risks.
Embracing tools like MyRecover empower users to recover deleted files and safeguard against data loss, ensuring a seamless computing experience on Windows devices.
FAQs:
1. Why doesn't deleting files free up storage space on my Windows device?
Deleting files may not always free up storage space due to several reasons such as temporary file accumulation, files lingering in the Recycle Bin, system restore points, large media files, and fragmented disk space. These factors contribute to inefficient storage utilization, causing the storage space to remain occupied despite file deletion.
2. How can I identify and remove temporary files that are consuming storage space?
To identify and remove temporary files consuming storage space on your Windows device, you can use the built-in Disk Cleanup utility. Simply search for "Disk Cleanup" in the Start menu, select the drive you want to clean, and let the utility scan for temporary files and other unnecessary data that can be safely removed to free up storage space.
3. What should I do if the Recycle Bin doesn't free up storage space after emptying it?
If the Recycle Bin doesn't free up storage space after emptying it, it may be due to files that were not permanently deleted.
To resolve this, right-click on the Recycle Bin icon on your desktop, select "Empty Recycle Bin," and then confirm the action to permanently delete all files from the Recycle Bin and reclaim the storage space.
4. Is it safe to adjust System Restore settings to reclaim storage space?
Yes, it is safe to adjust System Restore settings to reclaim storage space on your Windows device.
You can reduce the amount of disk space allocated for system restore points or disable System Protection for non-system drives to free up storage space. However, keep in mind that reducing the allocated space may limit the number of restore points available for system recovery in the future.
5. Can MyRecover retrieve files that were cleaned or deleted from my Windows system?
Yes, MyRecover is capable of retrieving files that were cleaned or deleted from your Windows system. MyRecover utilizes advanced algorithms to scan storage devices and recover deleted files efficiently.
By following simple steps, users can initiate a scan, preview recoverable files, and proceed with the recovery process to restore valuable data that was inadvertently deleted or cleaned from their Windows system.