To ensure data security, implement backup retention best practice can provides a strong foundation for data management. In order to achieve the goal, this article introduce you two considerations of retention policy and 5 backup retention best practices.

A backup retention policy outlines the guidelines and procedures for determining how long various types of backup data should be stored before they are deleted or archives. This policy specifies the retention duration for backups, the schedule for creating backups, and the specific data types that must be preserved.

When drafting a retention policy, admins must focus on two key factors: what data to retain which means the backup retention period and compliance.
What data to retain: Certain data must be retained by law for specific periods, while other data may be beneficial to keep but is not legally mandated by a retention policy.
Compliance: A primary reason for a company to retain data is to ensure compliance. Beyond internal compliance guidelines, various laws and regulations must be taken into account when developing a data retention policy.
For the in-depth nature of data retention policies, it’s important to follow some best practices when creating them. As you develop a backup retention policy for your organization, consider the following top five best practices outlined below.
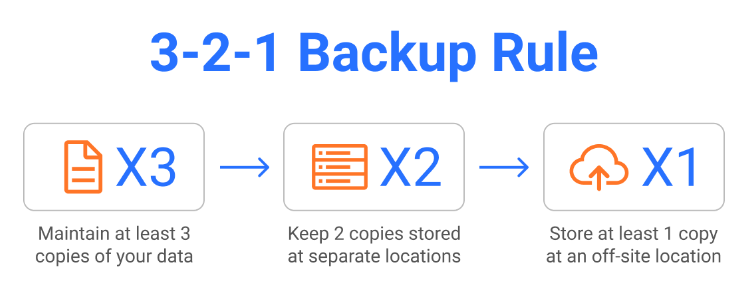
1. Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
❈ 3 Copies of Data: Maintain three copies of your data-one production copy and two backups.
❈ 2 Different Storage Media: Store backups on two different types of storage, such as disk and cloud, to minimize the risk of data loss.
❈ 1 Offsite Backup: Keep one backup offsite to protect against physical disasters.
2. Ensure You Understand the Type of Backup You Plan to Perform
Full backups, which include all existing files, are very time-consuming and should ideally be done only once. Incremental backups, which capture only changes since the last backup, are quicker but must be managed carefully to avoid consuming excessive bandwidth.
3. Understand the Backup Retention Period
Not all data needs to be stored for the same duration. After classifying your data, ensure that your retention policy specifies the storage period for each category accordingly.
✤ Short-Term Retention: Retain daily backups for a short period, e.g. 7–14 days, to enable quick recovery from recent incidents.
✤ Medium-Term Retention: Store weekly backups for a few weeks to a few months for less recent recovery needs.
✤ Long-Term Retention: Archive monthly or yearly backups for several years, depending on regulatory requirements and business needs.
4. Regularly Test Backup Restore
Determine when and how often you will perform backups, guided by your Recovery Point Objectives (RPO). If you are using traditional image-based backup tools, you may need to schedule backups during periods when your organization has the most available bandwidth. However, if you've transitioned to a cloud-first backup architecture, this concern will be significantly reduced.
5. Ensure Backup Security
✦ Encryption: Encrypt backups during transfer and at rest to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access.
✦ Access Control: Restrict access to backup systems and data to authorized personnel only, safeguarding against internal and external threats.
Following backup retention best practices provides several benefits that improve the overall effectiveness, security, and efficiency of your data management strategy. For a further data security, here it’s a high recommendation to a software - AOMEI Cyber Backup.
AOMEI Cyber Backup offers you a reliable ESXi backup for virtual machines. It provides a centralized console for creating backup tasks across multiple VMs, restoring entire VMs, and automating VM protection. It not only support VMware ESXi (6.0 and above) and Hyper-V (2012 and later), but also offer the following benefits:
✍ Flexible Retention Policies: Allow users to define and manage retention policies that suit their organization needs. This flexibility helps in optimizing storage usage and ensures that backups are retained for an appropriate duration. ✍ Agentless Backup: Create image-based backups of multiple VMs without the need to install an agent on each individual VM. ✍ Customizable Backup Scheduling: Schedule backups according to specific needs and retention periods, ensuring that critical data is regularly backed up, and old backups are pruned based on the defined policies. ✍ Multiple Storage Destinations: Backup VMs to local directories, network shared folders, and NAS shared folders.
You can click the button below to experience the 30-day free trial.
Follow easier steps to backup multiple ESXi VMs:
Step 1. Bind Devices
Access to AOMEI Cyber Backup web client, navigate to Source Device and click VMware > + Add VMware Device. Then enter device information and user information, and then click Confirm to Bind Device.
Step 2. Create Backup Tasks
Navigate to Backup Task > + Create New Task, and select Task Name, Device, Target, Archive, Schedule and Cleanup for your needs.
Target: Select to backup to a local path, or to a network path.
Archive: Click Backup Task > Backup Archive > Add New Archive, and then click Start to begin archiving.
Schedule: Perform full, differential, or incremental backup, and automate execution according to the frequency you specified.
Cleanup: Automatically delete the old backup copies that exceed the retention period you specified.
Step 3. Start Backup
Click Start Backup to select Add the schedule and start backup now, or Add the schedule only.
Backup tasks are listed and monitored individually, allowing for progress tracking, schedule adjustments, and restoration. Cloning a virtual machine to the same or a different datastore/host is simple—just click Restore to new location to create a clone without the need for reinstallation or configuration.
Implementing backup retention best practices is crucial for any organization seeking to safeguard its data, ensure compliance, and optimize operational efficiency. By balancing data availability with cost-effective storage solutions and adhering to regulatory requirements, organizations can mitigate risks, protect sensitive information, and maintain the integrity of their operations. Ultimately, these practices provide a robust framework for managing data in an increasingly complex and data-driven world.