Deleting a virtual machine (VM) in VMware needs to be performed with caution to avoid data loss or configuration issues. How to delete VM in VMware safely?

There are several reasons why you might need to delete a VM in VMware. These include reclaiming storage space, removing obsolete or unused VMs, and managing resource allocation more efficiently.
Before deleting a VM, it is crucial to take certain preparatory steps to ensure that no critical data is lost and that the deletion process goes smoothly.
After that, we will go to remove VM in VMware with detailed steps.
The easiest way to delete a virtual machine is to remove it directly from the inventory, but the virtual machine files remain in the datastore. This makes it easy for you to re-register the VM later via the datastore browser. This temporary way of removing a VM is useful when a VM reaches a license or hardware limit.
If you want to remove it permanently to free up datastore space, you need to further remove all its configuration files as well as snapshots from the datastore.
Next we will describe the steps to uninstall a virtual machine from VMware.
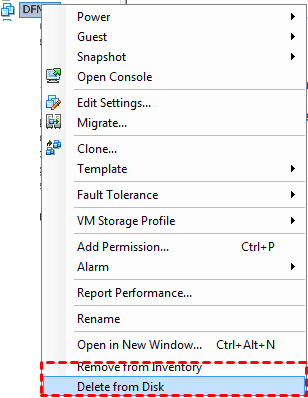
1. Log into the vSphere Client first, and locate the VM you want to delete.
2. Power off the virtual machine and right-click it.
3. To temporarily remove the VM, choose Remove From Inventory from the context menu, then click Yes.
To permanently delete it, choose Delete from Disk and click Yes.
For VMware Workstation 7.x and later versions, to remove a virtual machine: 1. To access the virtual machine, click it. 2. Click Manage in the Workstation menu bar. Choose Delete from disk. Select Yes. 3. Empty the Recycle Bin to free up the space in VMware Workstation. 📢 Also, do not forget to backup VMware Workstation before deleting the virtual machine.
VMware ESXi Shell and PowerCLI are powerful tools for managing VMs through command-line commands.
💡Using ESXi Shell to remove VM:
1. Enable SSH to your host as root, and enter the command to list all registered VMs.
2. Get the ID of the VM you removed the files for, and enter the command below to unregister that VM.
3. Remove the specified VM by entering:
4. Check if a VM has a snapshot:
5. Remove a snapshot of a VM:
💡Using PowerCLI to delete VM:
1. Connect to your vCenter Server. Get a listing of VMs on a host:
2. Delete a VM:
3. Check if a VM has a snapshot, and remove a snapshot of a VM:
✨Related: Another useful ESXCLI command ① Get the current power state of a VM: Get-VM –name vm_name ② Shutdown a VM: Shutdown-VMGuest –vm vm_name ③ Get the uptime for a VM: Get-Stat -entity vm_name -stat sys.uptime.latest -MaxSamples 1 ④ Reboot a VM: Restart-VMGuest –vm vm_name ⑤ Display the IP address of a VM: Get-VMGuestNetworkInterface –vm vm_name -guestuser guest_admin_user -guestpassword guest_admin_password
If a virtual machine is accidentally deleted, you can restore the vmdk file or snapshot to recover the virtual machine data.
To reduce license pressure and free up disk space, consider alternatives that may better suit your needs other than removing virtual machines. Backups are both a secure and highly cost-effective solution. At the same time, regular VM backups are also necessary for both businesses and individuals.
AOMEI Cyber Backup provides a comprehensive VMware backup solution that safeguards your VMs. It's another effective alternative to deleting VMs is to archive them to the cloud. By creating backups of your VMs, you also ensure that all important information is preserved, allowing for recovery if needed.
⊹ Automated Backup Scheduling: Set up automated backup schedules to regularly save the state of your VMs without manual intervention. ⊹ Archiving VMs: AOMEI Cyber Backup supports cloud archiving, allowing you to free up local storage while ensuring that your VM data remains accessible: ⊹ Centralized Management: Provides a centralized interface for managing backup tasks across multiple VMware ESXi hosts. ⊹ Quick Recovery: Facilitates quick recovery of virtual machines, minimizing downtime and ensuring business continuity.
AOMEI Cyber Backup supports both paid and free versions of VMware ESXi 6.0 and later versions. Next, I will demonstrate how to backup VMware ESXi VMs using AOMEI Cyber Backup. You can click the button to download the 30-day trial:
1. Bind Devices: Access to AOMEI Cyber Backup web client, navigate to Source Device > VMware > + Add VMware Device to Add vCenter or Standalone ESXi host directly. And then click … > Bind Device.
2. Create Backup Task: Navigate to Backup Task > + Create New Task, and select VMware ESXi Backup as the Backup Type.
3. Set Task Name, Device, Target, Schedule, and Cleanup as needed.
▶ Device: Navigate to the vCenter Server and bind to your device. With one click, you can easily backup multiple virtual machines.
▶ Target: Select to back up to a local storage, or to a network location.
▶ Archive (optional): Add an Amazon S3 bucket and archive VMware backup to AWS.
▶ Schedule (optional): Perform full, differential or incremental backup, and schedule backup daily, weekly or monthly according to the frequency you specified.
▶ Backup cleanup (optional): Configure a retention policy to auto delete old backup files and save storage space.
▶ Run Backup: Select to Add the schedule and start backup now, or Add the schedule only, and click Start Backup.
Created backup tasks will be listed and monitored separately, for restoring, progress checking and schedule changing.
4. Restore: Click Restore to recover a virtual machine from backup, saving the trouble of re-configuring the new VM.
☞ Once the backup task is created, it will be executed automatically according to your schedule. If you want to restore a virtual machine, you can click Restore and choose to restore entire VM to an available state from any historical restore point. ☞ In addition to restoring a VM to its original location, you can also choose Restore to new location, which will create a new identical VM directly from your backup to the target location.
Removing a virtual machine in VMware is a simple step, but it needs to be performed carefully to avoid data loss or system crashes. By following the steps outlined in this guide and creating a complete backup, you can manage your VMware virtual environment with confidence.