vCenter Server database is a important component of a vCenter Server instance. Before updating vCenter or deleting outdated data, you may want to backup vCenter database just in case. This article will show you how to backup vCenter embedded vPostgres and external MS SQL databases.

As the number of created virtual machines increases, your enterprise is likely to use VMware vCenter Server, the centralized management utility provided by the vSphere suite for managing multiple ESXi hosts, VMs, and other components.
vCenter Server requires a database to store and organize server data.
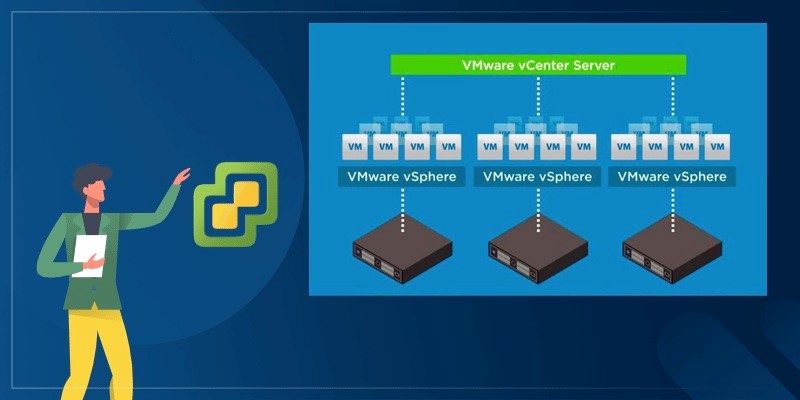
For vCenter Server on Windows, you can either use the bundled PostgreSQL database that can be installed and configured together with vCenter Server, or you can set up an external database prior to installing vCenter Server. vCenter Server for Windows supports Oracle and Microsoft SQL Server as external databases.
In vCenter, dozens of tables store information on resources, clusters, VMware Distributed Resource Scheduler, snapshots, VMware ESX hosts, virtual machines, alarms, performance statistics, tasks and events, and more. As the number of the hosts and VMs managed in your environment grows, the database can grow very large.
So, you may need to monitor the size of your vCenter Server database and regularly delete outdated data to save storage space, improve system performance, and reduce the chance of database corruption.
However, deleted data will be difficult to retrieve. To avoid accidental loss of important data, it is recommended that you back up vCenter database before performing a bulk delete or updating your vCenter Server.
Next, this article will show you the steps of how to backup vCenter database.
As you know, vCenter supports embedded vPostgres and external MS SQL or Oracle databases. And the ways to backup these 2 types of databases are different. Next, this part will show you the steps of how to backup vCenter database of these 2 types.
1. Log-in as an administrator to the Windows host machine on which vCenter Server is installed, navigate to C:\ProgramData\VMware\vCenter Server\cfg\vmware-vpx\ folder and then open the vcdb.properties file in a text editor.
2. In the vcdb.properties file, record the password for the vCenter Server database user.
3. Download the official package windows_backup_restore.zip attached to VMware’s KB article and extract is on the vCenter Server.
4. Open a Command Prompt and navigate to the following location:
%VMWARE_CFG_DIR%\python
5. Run the following command using the vCenter password you recorded to start backup:
python.exe c:\path_to_script\backup_win.py -p "password" -f c:\path_to_backup_folder\backup_VCDB.bak
For example:
python.exe c:\backup_win.py -p "s_PJmbGzC83QRYlp" -f c:\backup_VCDB.bak
Once the backup completes, you see a message that the backup completed successfully.
1. Open Microsoft SQL Server Management Studio Express and connect to the vCenter Server database server or instance.
Note: If you are not using a dedicated SQL server, the database resides on vCenter Server. To verify the location and database name: 1. Open the ODBC connector. 2. Click the System DSN tab. 3. Find the vCenter Server item. 4. Click configure. 5. Proceed through the steps and note the SQL Server and the default database.
2. Stop all vCenter Server services on the vCenter Server system, to ensure that no service is out of sync during the backup.
3. Expand Databases and look for the vCenter Server database, the default name is VIM_VCDB.
4. Right-click the vCenter Server database and then click Tasks > Back Up.
5. Select your backup options and Click OK.
Remember to copy the backup file to a safe location during maintenance or upgrades, and ensure to perform this backup before performing any operation on vCenter Server, as it holds current and historical data.
vCenter Server is a very convenient official platform for centrally managing ESXi virtual environments and large numbers of VMs on it. The free VMware backup software - AOMEI Cyber Backup enables you to backup multiple VMs either managed by vCenter Server, or on a standalone ESXi host directly and easily.
✦ Agentless Backup: create complete and independent image-level virtual machine backup in VMware ESXi and Hyper-V. ✦ Multiple VM Backup: batch backup large numbers of VMs managed by vCenter Server, or multiple VMs on a standalone ESXi host. ✦ Multiple Storage Destinations: backup to a local drive, or network destinations like NAS. ✦ Automated Execution: create backup schedules to automate backups daily, weekly, or monthly. ✦ Restore Entire VM: restore instant available VMs from any selected restore points to an original or new location.
Each vCenter Server instance requires a database to store the performance data, logs of tasks that were performed, and logs of events that occurred. Before you want to update vCenter or cleanup outdated data, you may want to perform vCenter database backup in advance.
vCenter Server support both embedded and external databases. This article showed the steps on how to backup vCenter databases accordingly. You can read the interested part depending on your situation.