Learn how to effectively configure and manage Distributed Resource Scheduler (DRS) in VMware for efficient workload distribution and performance optimization in virtualized environments.

VMware DRS, which is short for Distributed Resouce Scheduler is a clustering feature within VMware vSphere that automatically balances computing workloads with available resources in a virtualized environment.

► Load Balancing: DRS monitors the resource usage such as CPU, memory, etc. of virtual machines and the hosts in the cluster. If it detects an imbalance of workloads, it automatically migrates VMs from heavily loaded hosts to less loaded ones using VMware vMotion.
► Allocate resources: DRS creates resource pools with specific resource limits and shares. This allows administrators to allocate resources to different parts or applications according to their importance or requirements.
► Effective monitoring and control: VMware DRS offers centralized control of resource pools to increase your VM performance.
► affinity or anti-affinity rules: These files help you control the placement and distribution of VMs across hosts within a cluster, depending on your specific needs.
The affinity rule is to keep certain VMs together on the same host. This is useful when you want a set of VMs to run on the same host to reduce network latency and ensure better performance.
And the anti-affinity rule is to ensure that certain virtual machines (running the same service) are kept in separate hosts. This works if one host fails, and not all instances of a critical service are lost.
► Maintenance Mode Assistance: When a host is placed into maintenance mode, DRS automatically moves VMs off the host to other hosts in the cluster to allow for maintenance without downtime.
Then there are the steps to enable VMware DRS.
Go to the vSphere Web Client or vSphere Client > On the left "Hosts and Cluster" view, expand the vCenter Server icon and right-click on the "Datacenter". > select "New Cluster." > Follow the prompts to specify the cluster name, select the desired hosts, and complete the cluster creation process.
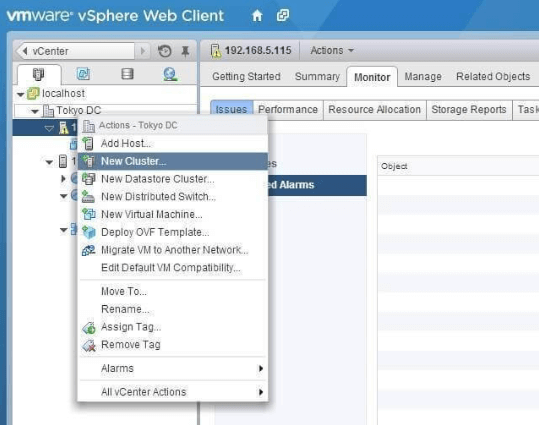
Then expand the DRS menu, and check the "Turn on" option.
Once the DRS cluster is created, you can configure the automation level for workload distribution.
There are five automation levels to choose from:
Select the appropriate automation level that aligns with your workload requirements and operational preferences.
Migration thresholds determine the sensitivity of DRS in triggering workload migrations. You can adjust the thresholds based on your desired level of workload balancing. There are three migration threshold settings:
Evaluate your workload patterns and select the migration threshold that best suits your environment's needs.
DRS affinity rules help control the placement of VMs within the DRS cluster. Affinity rules can be used to enforce VM-to-VM or VM-to-host relationships. For example, you can create an affinity rule to keep two VMs together on the same host or separate them onto different hosts. By defining these rules, you can ensure that certain VMs are always placed together or apart, based on your requirements.
After configuring DRS, it is important to regularly monitor and manage its performance. Keep an eye on the DRS cluster's CPU and memory utilization, as well as the distribution of VMs across hosts. Use vSphere's DRS-related monitoring tools and performance charts to gain insights into resource usage and make necessary adjustments. Regularly review and fine-tune DRS settings based on workload changes and performance observations.
To optimize DRS configuration, consider the following best practices:
While DRS is designed to enhance workload distribution, issues may arise. Here are a few common challenges and troubleshooting tips:
VMware DRS cluster is a useful tool to manage your VM resource, and it provides some features to ensure your business runs properly. However, when it comes to the VM security, these are not enough. Usually, you will need a professional VM backup solution.
For example, AOMEI Cyber Backup. This powerful and user-friendly backup software enables you to create a VMware backup schedule to run backup task automatically. When you encounter a system crash, or data loss, it can quickly restore your VMware virtualized environment with VM backups. In this part, we will guide you on how to back up and protect your VMware VMs easily.
Step 1. Download, install, and run AOMEI Cyber Backup on a Windows or Linux computer.
Step 2. In this AOMEI Cyber Backup console, click "Source Device" > "VMware" > "+ Add VMware Device" to enter vCenter or Standalone ESXi host to add VMs > "Confirm".
Step 3. Click "Backup Task" on the left pane > "+ Create New Task". Choose "VMware Backup" as the backup type. Then choose target, content, and other information according to the settings.
Step 4. Click "Start Backup" to initiate the backup process.
Step 5. When you need a restore, you can click the 3-dot icon and click "Restore".
This article introduces the VMware distributed resource scheduler and guides you on how to configure DRS in VMware to make the most of your VMware environment and achieve enhanced performance and resource efficiency.
Besides, to protect VMware VMs and ensure business continuity, it is necessary to backup virtual machines with AOMEI Cyber Backup. It provides a centralized way to backup and restore all VMware ESXi. Besides VMware, this solution also supports Hyper-V backup, Windows PCs and server backup, MS SQL server backup.