Moving vCenter to a new host is a critical task that requires careful planning and execution. We'll provide you with step-by-step instructions and an alternative method for migrating vCenter.

Moving vCenter to a new host is a decision organizations often make to address various challenges and leverage the benefits of a more robust infrastructure. There are several reasons why organizations consider this migration:
In this article, we will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to move vCenter to new host whether you have VMotion or not.
Moving vCenter 7 to another host using vCenter itself is a reliable and efficient method. Follow these step-by-step instructions to ensure a smooth migration process:
Before starting the migration process, there are a few prerequisites and considerations to keep in mind:
1. Install a new vCenter server on the target host using the installation wizard.
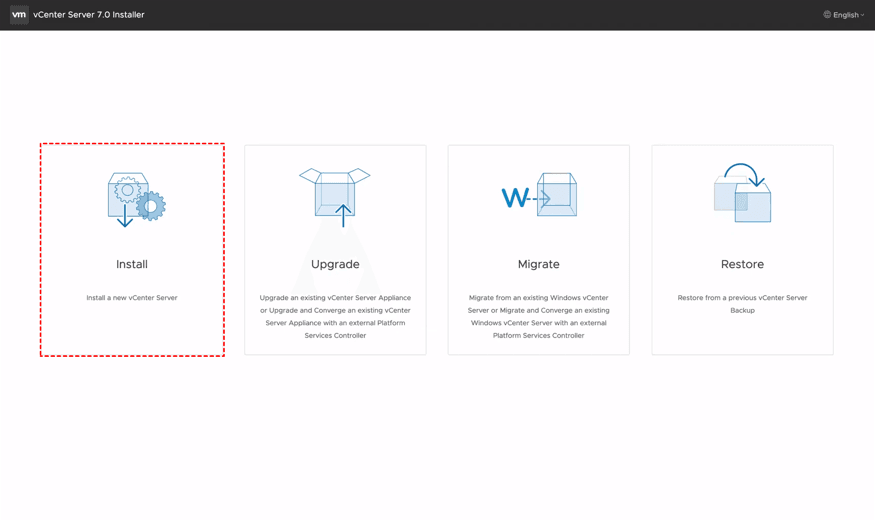
2. Follow the prompts and provide the necessary information, such as server name, IP address, and administrative credentials.
3. Configure network settings, such as IP addresses, DNS, and gateway, for the new vCenter server.
1. Connect to both the source and target vCenter servers using the vSphere Web Client.
2. In the vSphere Web Client, navigate to the "vCenter Server" inventory object in the source vCenter.
3. Select "Migrate vCenter Server" from the "Actions" menu.
4. Follow the migration wizard to select the destination vCenter server and choose the components to migrate. Typically, you would select all vCenter components, including hosts, datacenters, clusters, and virtual machines.
5. Review the migration summary to ensure that everything is configured correctly.
6. Initiate the migration process and monitor the progress until it completes successfully. This process may take some time, depending on the size and complexity of your vCenter environment.
1. Once the migration is complete, verify that all vCenter components have been successfully migrated to the new host. Check that hosts, datacenters, clusters, and virtual machines appear in the new vCenter server.
2. Test the functionality of the migrated components to ensure that everything is working as expected. Verify that you can power on and manage virtual machines, access datastores, and perform other administrative tasks.
1. After verifying the successful migration and ensuring that everything is functioning correctly, it's time to decommission the source vCenter server.
2. Ensure that all critical components and data have been migrated to the new host and double-check for any potential dependencies.
3. Follow proper procedures to remove the source vCenter server from the environment. This may involve disconnecting hosts, removing vCenter services, and uninstalling the source vCenter server software.
Here's a step-by-step guide to help you migrate VCSA to a new host without using VMotion.
1. Access the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
2. Navigate to the vCenter Server Appliance (VCSA) you wish to migrate.
3. Right-click on the VCSA and select "Export OVF Template."
4. Follow the prompts to specify the export location and provide a name for the OVF template.
5. Wait for the export process to complete. This may take some time, depending on the size of your VCSA.
1. Access the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client on the new host.
Select the new host as the deployment target.
2. Right-click on the host and choose "Deploy OVF Template."
3. Specify the path to the exported VCSA OVF template file.
4. Follow the deployment wizard, providing necessary information such as the name, network configuration, and storage settings.
5. Review the configuration details and complete the deployment process.
1. Power on the newly deployed VCSA.
2. Access the VCSA management interface using a web browser and log in with administrative credentials.
3. Configure the network settings for the new VCSA, ensuring it is on the same network as the existing VCSA.
4. Apply any necessary customizations, such as IP addresses, DNS, and gateway settings, to match the existing VCSA configuration.
1. Access the existing VCSA using SSH or the console.
2. Use the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface (VAMI) to export the VCSA configuration.
3. Transfer the exported configuration file to the new VCSA using secure file transfer protocols (e.g., SCP).
4. Access the new VCSA using SSH or the console.
5. Use the vCenter Server Appliance Management Interface (VAMI) to import the configuration file.
6. Verify that the imported configuration matches the settings of the existing VCSA.
1. Update the DNS settings of the new VCSA to ensure it resolves correctly.
2. Validate the connectivity of the new VCSA by accessing the vSphere Client or vSphere Web Client.
3. Test the functionality of the new VCSA by performing administrative tasks, managing virtual machines, and accessing vCenter services.
By following these steps, you can successfully migrate VCSA to a new host without using VMotion.
Taking backups of vCenter VMs before migration is crucial for ensuring data integrity and minimizing the risk of data loss or complications during the process. Following best practices such as using reliable backup solutions -AOMEI Cyber Backup which schedules regular backups to enhance the effectiveness of vCenter VM backups.
With AOMEI Cyber Backup, you could enjoy the following features:
✦ Agentless Backup: create complete and independent image-level backup for VMware ESXi and Hyper-V VMs. ✦ Support Free ESXi: support both paid and free versions of VMware ESXi. ✦ Batch VM Backup: batch backup large numbers of VMs managed by vCenter Server, or multiple VMs on a standalone ESXi host. ✦ Multiple Storage Destinations: backup to local or network share destinations. ✦ Automated Execution: create backup schedules to automate virtual machine protection. ✦ Role Assignment: allows one administrator to create sub-accounts with limited privileges.
AOMEI Cyber Backup supports VMware ESXi/Hyper-V backup as well as SQL Server database backup. Next, I will show you how to back up VMware ESXi VMs with AOMEI Cyber Backup in 3 simple steps. You can click the following button to download the 30-day free trial.
1. Add devices: download AOMEI Cyber Backup and click Source Device >> VMware >> + Add VMware Device to Add vCenter or Standalone ESXi host. And then click … > Bind Device.
2. Create backup task: click Backup Task >> Create New Task.
3. Restore: click “…”>> Restore to select restoration content and destination.
You can choose to Restore to original location. It allows you to recover entire VM easily and quickly. It saves time to recreate or configure ESXi virtual machines.
Or you can also restore to new location to create a new VM in the same or another datastore/host directly from the backup, saving the trouble of re-configuring the new VM.
Moving vCenter to a new host is a process undertaken by organizations to improve performance, scalability, and infrastructure. By migrating vCenter, organizations can overcome hardware limitations, resource constraints, and leverage better infrastructure.
There are different methods to migrate vCenter to new host, such as using vCenter itself or migrating VCSA without VMotion. It is crucial to take backups of vCenter VMs before migration to ensure data integrity. A well-planned migration process minimizes disruptions and ensures a seamless transition. Proper planning, testing, and post-migration optimizations are essential for a successful move.
Prioritizing backups safeguards your data and facilitates a secure transition to the new host.