Admins who connect AD with vCenter Server can grant users authorization for and access to VMs, storage and compute resources in vSphere. Using Active Directory for authentication provides more robust account management capabilities.

VMware vCenter Server has an internal user database that allows you to add and manage users very easily. Built-in users, groups and roles come preconfigured when you first install vCenter Server. However, you can use Microsoft Active Directory (AD) as a source of identity for authentication purposes. With Active Directory integration, vCenter Server manages access to VMs, storage and compute in vSphere based on AD users and groups. Active Directory's login information supersedes the built-in VMware user login info.
In a large environment, you might want to connect your virtualization infrastructure to a centrally manage Active Directory. This article explains how to add active directory authentication in vCenter 7.0.
It is convenient once you add vCenter to active directory. Because you can share the connection URL to vCenter Server with your co-workers within the company, who will then be able to log in with their Windows session authentication without reentering their login and password combination.
1. From the vSphere Client and login as Single Sign-On Administrator (Password set during installation).
2. Navigate to Menu >> Administration >> Single Sign-On >> Configuration.
3. Click the Identity Provider tab, and open Identity Sources.
4. Click ADD.
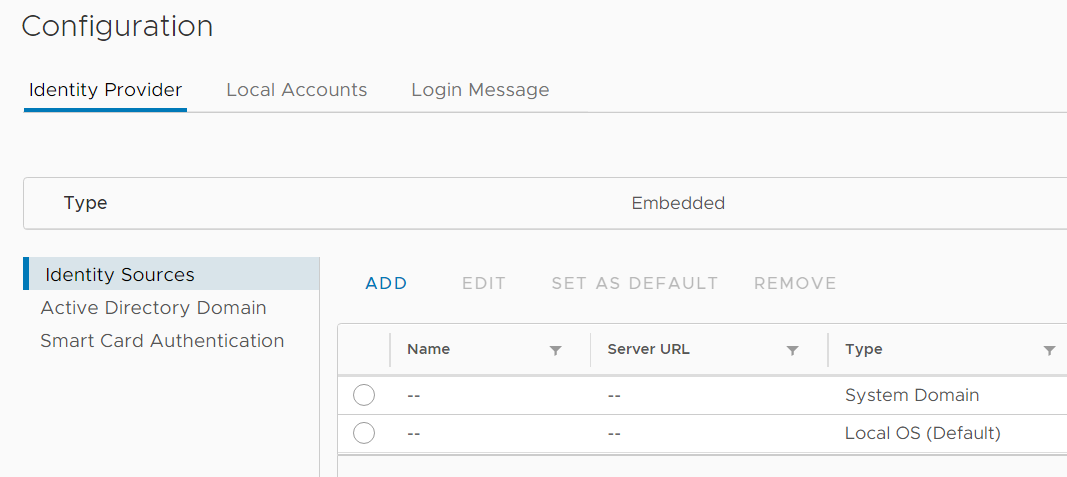
5. Start adding identity source appropriately:
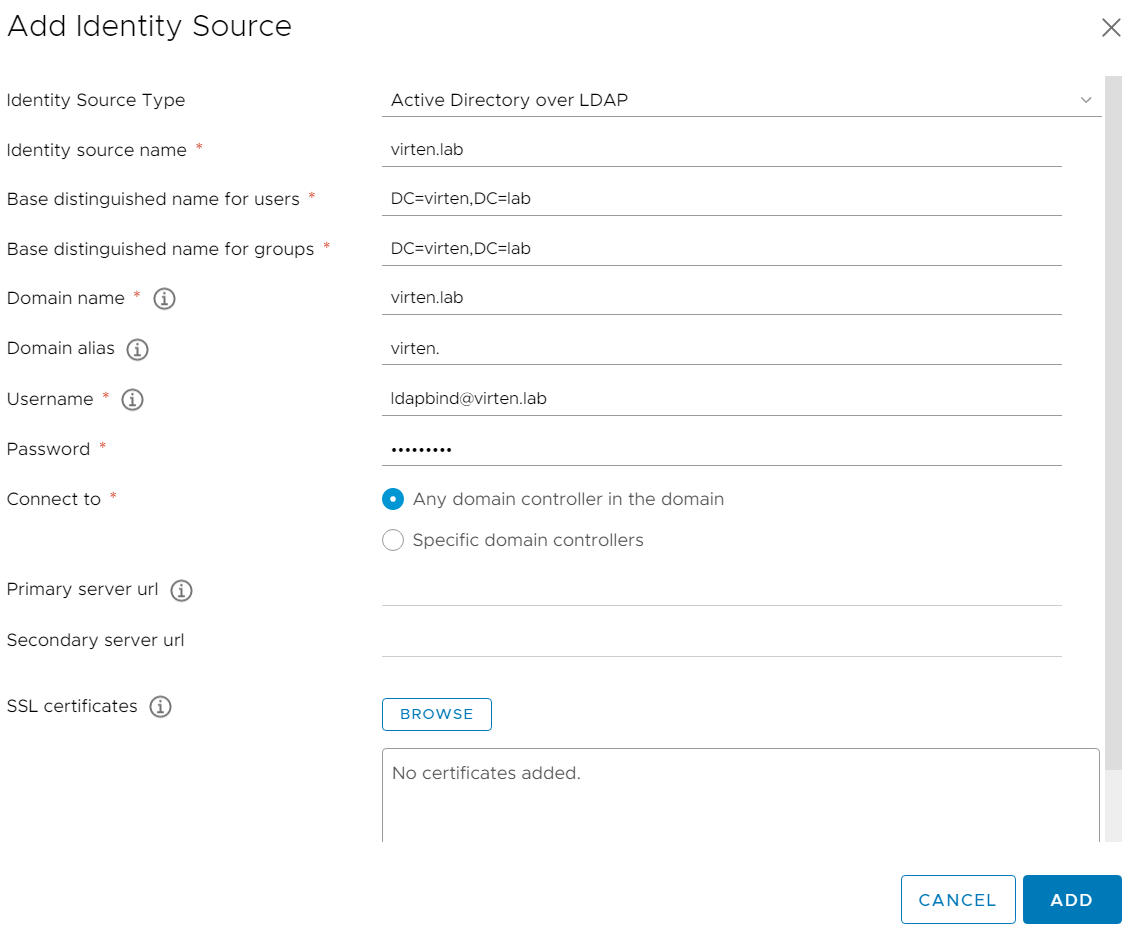
6. Back at Identity Sources your AD should appear in the list and from now on you are able to assign vCenter permissions to users and groups from your active directory.
7. Select your Active Directory and click the SET AS DEFAULT button to make it to your vCenters default domain for authentication which means that everyone who does not specify the domain name to log in gets automatically authenticated against this domain.
8. To log in with AD users, you have to set permissions. To add an AD User/Group as Global Administrator, navigate to Administration >> Access Control >> Global Permissions.
9. Click Add permission
10. Select the domain and start typing in the User/Group search field to select a Domain entity.
Now, log in from a Windows computer attached to the Microsoft domain where you opened a session as an administrator. And verify if you successfully logged in as an AD administrator, checking the top right corner of your vSphere Client interface.
You could add any users or groups from AD and give them access to VMs via the vSphere web client. Once integrating vCenter with active directory, users and groups don't have to install additional software or remember other passwords to work with VMs.
In addition to this, most users utilize centralized backup software to manage vCenter VM backup in bulk.
If you only own 1 or 2 devices, you can clone virtual machines, copy virtual machine disk files and export VM as OVF template to complete ESXi backup. However, for long-term data protection, it is better to use a professional virtual machine to create standalone and automated backups. Here, I will try a professional and VMware backup tool – AOMEI Cyber Backup to perform automated backups for multiple virtual machines. It supports various versions including ESXi 6.0-7.0, and it offers automated backup task and instant disaster recovery. You are able to back up your multiple virtual machines with its flexible strategies.
With AOMEI Cyber Backup, you can enjoy these features easily.
Secure VM Backup: schedule VMware or Hyper-V virtual machine backups and perform centralized and auto backup to protect crucial data continuously without human errors. Flexible vSphere Backup: batch backup large numbers of VMs managed by vCenter Server, or multiple VMs on a standalone ESXi host. Instant Disaster Recovery: instantly restore the whole virtual machine to the previous state from any selected history version. Role-Assignment: allow one administrator to create sub-accounts with limited privilege, effectively reduce administration cost and manual errors. Free ESXi Backup: support the free version of ESXi backup.
Please hit the button below to download and use AOMEI Cyber Backup 30-day free trial:
*You can choose to install this VM backup software on either Windows or Linux system.
If you want to protect the security of your virtual machines comprehensively, please refer to the following steps.
1. Add devices: download AOMEI Cyber Backup and click Source Device >> VMware >> + Add VMware Device to Add vCenter or Standalone ESXi host. And then click … >> Bind Device.
2. Create backup task: click Backup Task >> Create New Task.
★ Enter task name and batch select large numbers of VMs managed by vCenter Server for centralized backup.
★ Schedule: schedule backup as full / incremental / differential backup and specify time to run the backup.
★ After configuring the backup task, review the information and click Start Backup.
3. Restore: click “…”>> Restore to select restoration content and destination.
You can choose to Restore to original location. It allows you to recover entire VM easily and quickly. It saves time to recreate or configure ESXi virtual machines.
Or you can also restore to new location to create a new VM in the same or another datastore/host directly from the backup, saving the trouble of re-configuring the new VM.
The vCenter Server for Windows must ensure users are authenticated with an individual authenticator prior to using a group authenticator. This article offers detailed steps to add active directory authentication in vCenter, which helps to provide more robust account management capabilities in a large environment.