VMware ESXi command line is powerful and efficient tool to manage virtual machines. In this article, you will know the essential and useful command line to directly get information without GUI.

VMware vSphere supports several command-line interfaces to manage your virtualization infrastructure, including the vSphere Command-Line Interface (vCLI), ESXi Shell command, and PowerCLI. VMware command line is a powerful tool that performs vSphere, including hosts, networks, storage, virtual machines, guest operating systems, and more.
If you heard about ESXi command line, you may know that ESXi has its own ESXCLI commands. The ESXi Shell is disabled for the security purpose on ESXi hosts. You can enable local and remote access to the shell if necessary. This article will introduce the how to list VMware VMs using commands and the useful ESXCLI command lines.
Tips: To reduce the risk of unauthorized access, it's recommended to enable the ESXi Shell for troubleshooting only.

As we mention, by default, ESXi Shell is disabled for local and remote access, so you should enable it first.
Enable SSH session with root access:
In VMware vSphere Client, navigate to Hosts and Clusters and select your ESXi host, then click Service >> Configure >> SSH. Click Start to launch the SSH server once.
Tips: On Windows, you can use PuTTY as an SSH client for running ESXi shell commands remotely.
Type the following command to get a list of all registered virtual, identified by their VMID, Display Name and path to the .vmx configuration file:
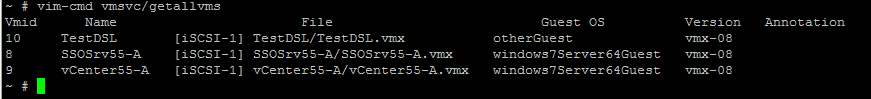
In VMware, using esxcli list VMs is able to list all the virtual machines. Besides, there are some other useful commands used in VMware ESXi, please continue to read this page.
In the former part, I have introduced how to list virtual machines in VMware using commands. Then you may want to know some other useful command line. For example, how to list running VMs on ESXi, how to power off VM from ESXi command line, etc., how to get VM/host information directly.
✦ List running VMs on ESXi with commands
You can easily list all running virtual machines on the host from a shell prompt without accessing GUI by typing the following command:
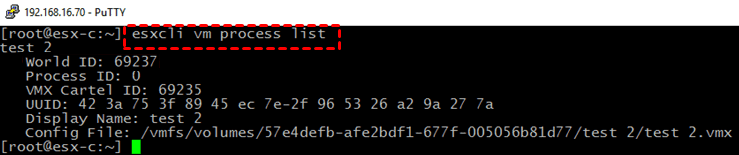
The World ID can be used with other ESXCLI commands to carry out various tasks related to VMs.
✦ Power-off VM from ESXi ESXCLI command
The esxcli command can be used locally or remotely to power off a virtual machine running on ESXi 5.x or later.
Power off the virtual machine from the list by running this command:
esxcli vm process kill --type= [soft,hard,force] --world-id= WorldNumber
✦ Power on/off a virtual machine using ESXi command line utility vim-cmd
If you are using ESXi 4.x or later, you can also use these command line to power on/off a virtual machine:
1. List the inventory ID of the virtual machine with the command:
Note: The first (leftmost) column of the output shows the vmid.
2. Check the power state of the virtual machine with the command:
Power-on the virtual machine using ESXi command line:
Power-off the virtual machine with the command:
#1: esxcli vm
Description: Lists virtual machines and shutting them down forcefully.
#2. esxcli system version get
Description: Returns the ESXi build and version numbers.
#3: esxcli system hostname get
Description: Returns the hostname, domain and FQDN for the host.
#4: esxcli system stats installtime get
Description: Returns the date and time of when ESXi was installed.
#5: esxcli hardware
Description: Hardware namespace. Used primarily for extracting information about the current system setup.
#6. esxcli network
Description: Network namespace for managing virtual networking including virtual switches and VMkernel network interfaces.
#7. esxcli system
Description: System monitoring and management command.
#8: esxcli storage vmfs extent list
Description: The command generates a list of extents for each volume as well as the corresponding device name to UUID mapping.
After knowing the VMware list VM command line and other useful VMware ESXi command line, you can easily manage your virtual machines in VMware. However, for many users, it’s difficult to master so many command lines proficiently, and any human error may cause system or disk corruption, thus resulting in virtual machine data loss and enterprise financial damage.
So, in order to provide a secure insurance for your VMs, I suggest that you can make a virtual machine backup in your work routine.
Before making big changes, a backup of the virtual machine is needed, especially when using unfamiliar VMware commands, since it is likely to cause damage to your virtual machines. Here, I’d like to apply AOMEI Cyber Backup, a free VMware backup software, to provide continuous protections for virtual machines. With this professional tool, you can get the following benefits.
✔ Support Free ESXi: AOMEI Cyber Backup supports both paid and free versions of VMware ESXi. ✔ Flexible Backup Scheduling: This feature enables you to design personalized backup schedules that guarantee backups happen at opportune times. ✔ Centralized Management: AOMEI Cyber Backup offers a centralized console to manage backup tasks, check status, and configure settings. ✔ Cloud Storage: Support archiving VM backup versions to an Amazon S3 storage. ✔ Fast Disaster Recovery: Instantly restore the whole virtual machine to the previous state or restore it to another host based on a few clicks. ✔ Role Assignment: allows one administrator to create sub-accounts with limited privileges.
Create a secure backup task that covers multiple ESXi VMs. You can click the following button to download the perpetual Free Edition:
*You can choose to install this VM backup software on either Windows or Linux system.
One quick virtual machine backup software
1. Bind Devices: Access to AOMEI Cyber Backup web client, navigate to Source Device >> VMware / Hyper-V to add a host. Take VMware as an example, you can Add vCenter or Standalone ESXi for VMs backup.
2. Click Backup Task > Create New Task to set up the backup task as you need.
3. Start Backup: Click Start Backup and select Add the schedule and start backup now, or Add the schedule only.
✎ In addition to the basic features, you can also upgrade to enjoy advanced functions: ✦ Batch VM backup: batch backup large numbers of VMs managed by vCenter Server or on standalone ESXi hosts. ✦ Backup Cleanup: You can specify a retention policy, and the old backup files that exceed the period will be automatically deleted. ✦ Restore to new location: If your original VM corrupts, you can easily restore VM to its previous place or to another datastore/host without any complicated configuration and reinstallation.
This article provides useful command line such as VMware list VMs command line. Using esxcli list vms is convenient to manage VMware virtual machines directly without GUI.
Meanwhile, when using ESXCLE command, you should prepare a VMware backup solution in case of VM data loss.